For all the young chemists , we have finally entered into the field of chemistry!!

As always we will start with the basics i.e. Chemical Reactions and Equations.
Now, what is really a chemical reaction?
A chemical reaction a process during which the chemical and some physical properties gets changed. And What are chemical and physical properties?

The chemical property of a substance generally denotes its properties at the atomic level and the physical properties are all those quantities which we study in physics like temperature, shape ,etc.
That’s all right but the next question arises that how will we identify if the changes in a chemical reaction are in the atomic level?
These are a few indicators that a chemical reaction is taking place-
- Change in colour.
- Change in temperature.
- Evolution of a gas.
- Change in smell.
- Change in taste.
Chemical reactions are basically divided into the following types on the basis of the changes in atomic level-
- Combination reaction
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/acid-and-base-combined-58dad2a63df78c5162f364e6.jpg)
Combination reaction is a type of reaction in which two compounds give rise to a single compound upon reacting like the following:-
- Na2 + H2O -> 2NaOH. Here sodium oxide is combined with water gives sodium hydroxide.
- 4Li + O2 -> 2Li2O. Here lithium is combined with oxygen to form lithium oxide.
- 2Mg + O2 -> 2 MgO.
- H2 + Cl2 -> 2 HCL.
- NH3 + HCl -> NH4Cl.
- 2H2 + O2 -> 2 H2O.
- S + O2 -> SO2.
- Ba + F2 -> Ba F2.
- Decomposition Reactions
Decomposition reaction is a type of reaction in which a single compound breaks down into Multiple compounds upon exposure to some source of energy .
Few types of decomposition on the basis of the type of energy needed are as follows:-
Thermal decomposition – such reactions are usually endothermic, since energy in the form of heat is required to break the bonds of the more complex molecule. Examples include
CaCO3(s)+heat → CaO(s) + CO2(g) – calcium carbonate decomposes into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide when heated;
2KClO3(s) + heat → 2KCl(s) + 3O2(g) – potassium chlorate decomposes into potassium chloride and oxygen gas when heated;
2Fe(OH)3+heat→Fe2O3+3H2O -ferric dioxide decomposes into ferric oxide and water when heated.

Electrolytic decomposition – such reactions occur when an electric current is passed through an aqueous solution of a compound. Two examples of this type of decomposition are the electrolysis of water and the decomposition of sodium chloride
2H2O(l) → 2H2(g) + O2(g) – water decomposes into hydrogen and oxygen in the presence of an electric current;
2NaCl(l) → 2Na(l) + Cl2(g) – molten sodium chloride will decompose into molten sodium and chlorine gas;
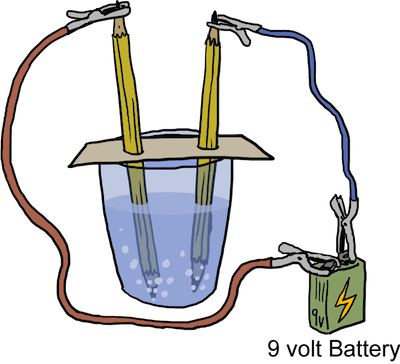
Photo decomposition – these reactions occur in the presence of light (photons). The photons helps to break the bonds between the atoms in this type of reaction. Examples include
2AgCl(s) + sunlight → 2Ag(s) + Cl2(g) – silver chloride decomposes into silver and chlorine in the presence of sunlight;
2AgBr(s) + sunlight → 2Ag(s) + 2Cl2(g) – silver bromide decomposes into silver and chlorine in the presence of sunlight.
- Displacement Reaction
As the name suggests this reaction has something about displacing atoms or you can say an exchange of elements in the compounds.
It is divided into two different types of displacement reactions:-
- Single Displacement.

In this type of reaction an element displaces another element from its salt solution according to the reactivity series. i.e. The element can only displace the other from its salt solution if it is more reactive than that element.
Examples-
- Fe + CuSO4 🡪 FeSO4 + Cu.
- 2K + MgCl2 🡪 2KCl + Mg.
- AgNO3 + NaCl 🡪 AgCl + NaNO3.
- Zn + CuSO4 🡪 ZnSO4 + Cu.
- Cu + 2AgNO3 🡪 CuNO3 + 2Ag.
- Fe + CuSO4 🡪 FeSO4 + Cu.
- Pb + CuCl2 🡪 PbCl2 + Cu.
- Cl2 + 2NaBr 🡪 2NaCl + Br2.
- Double displacement reaction
/experiment-showing-how-miscible-liquids-react-the-coloured-pigments-diffuses-over-time-until-evenly-distributed-in-the-water-creating-a-mixture-of-the-two-colours-123535153-572f8ecc5f9b58c34cabc582.jpg)
In this type of reaction elements from two compounds displace each other from their salt solutions according to the reactivity series as follows:-
Pb(NO3)2 (aq)+ 2NaCl (aq) ⇌ 2NaNO3(aq)+ PbCl2(s)
H2SO4(aq) + 2LiOH (aq) ⇌ Li2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
AgNO3 (aq) + HCl (g) ⇌ AgCl(s) + HNO3(aq)
- Redox Reactions
The last type of reactions based on this classification is the Redox Reactions.
It will be discussed in the next post in detail.
